The Digestive Disease Data Science Commons: Host Datasets
CSIBD investigators focus on a comprehensive approach for investigating the basis of human disease, going beyond massively parallel sequencing to dissect cellular circuitry in order to make functional genotype-phenotype connections. Studies are geared toward identifying the role of disease-linked functional variants in order to uncover therapeutic targets.
Raw data links will take you to public access (e.g. GEO, SRA) and protected (e.g. DUOS, dbGAP) repositories. Please note that DUOS links in this page will direct you to the DUOS landing page. Once you sign in to DUOS, you should arrive at the data library page in which you can use the search bar to look up the study you are interested in (e.g. search ‘000146’). Like dbGAP, DUOS hosts protected clinical data and additional permissions are required for access as explained in their step by step tutorial.
Featured Studies |
|---|
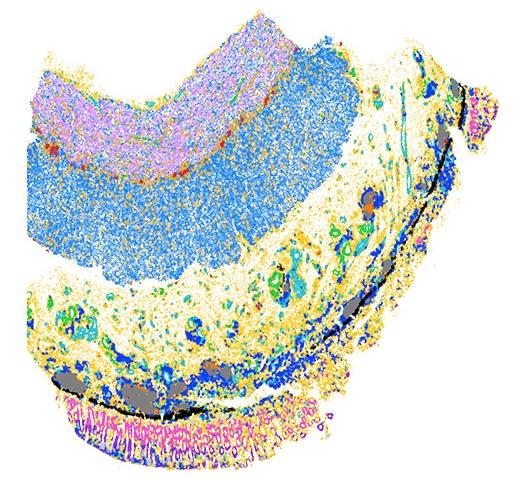
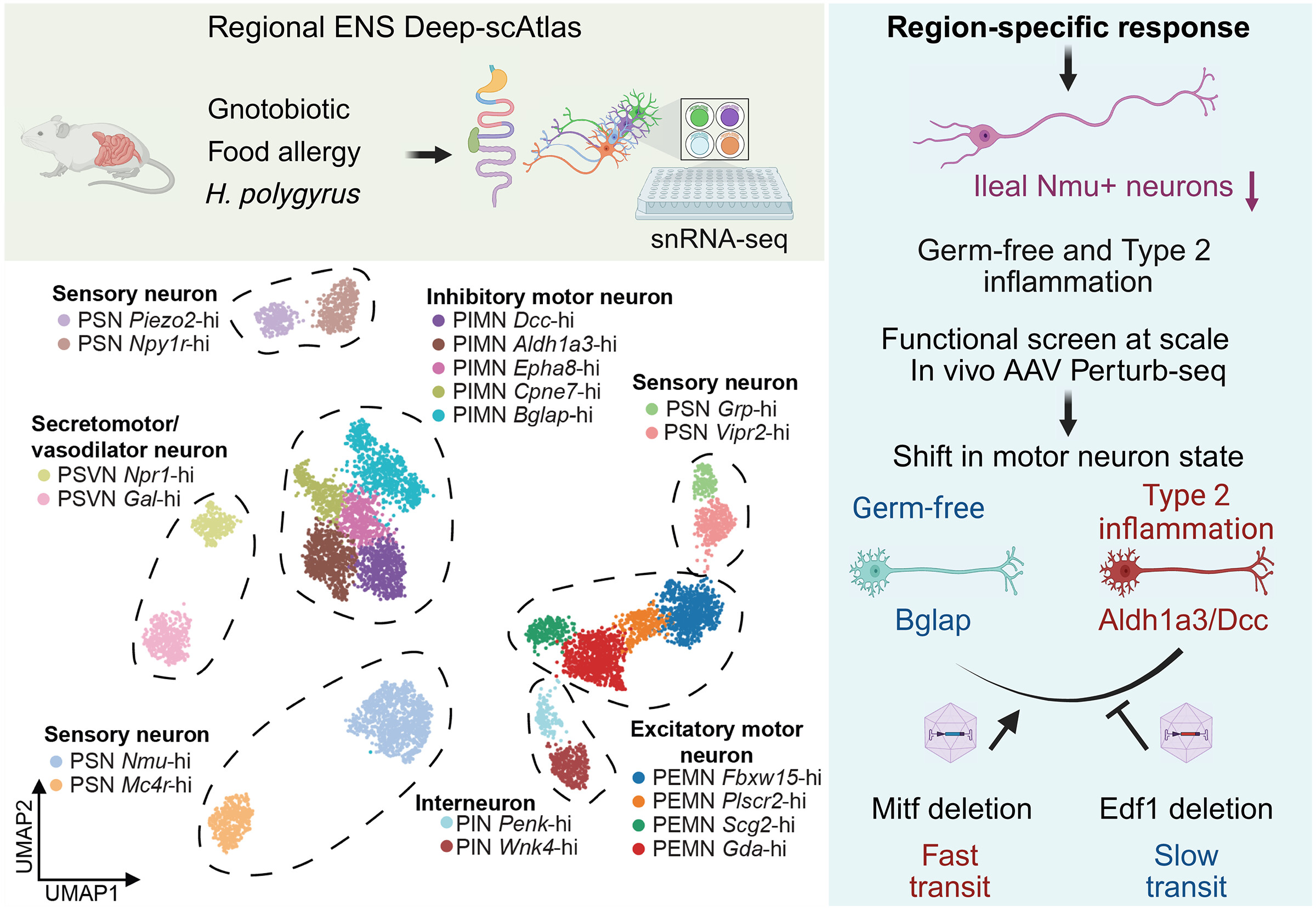
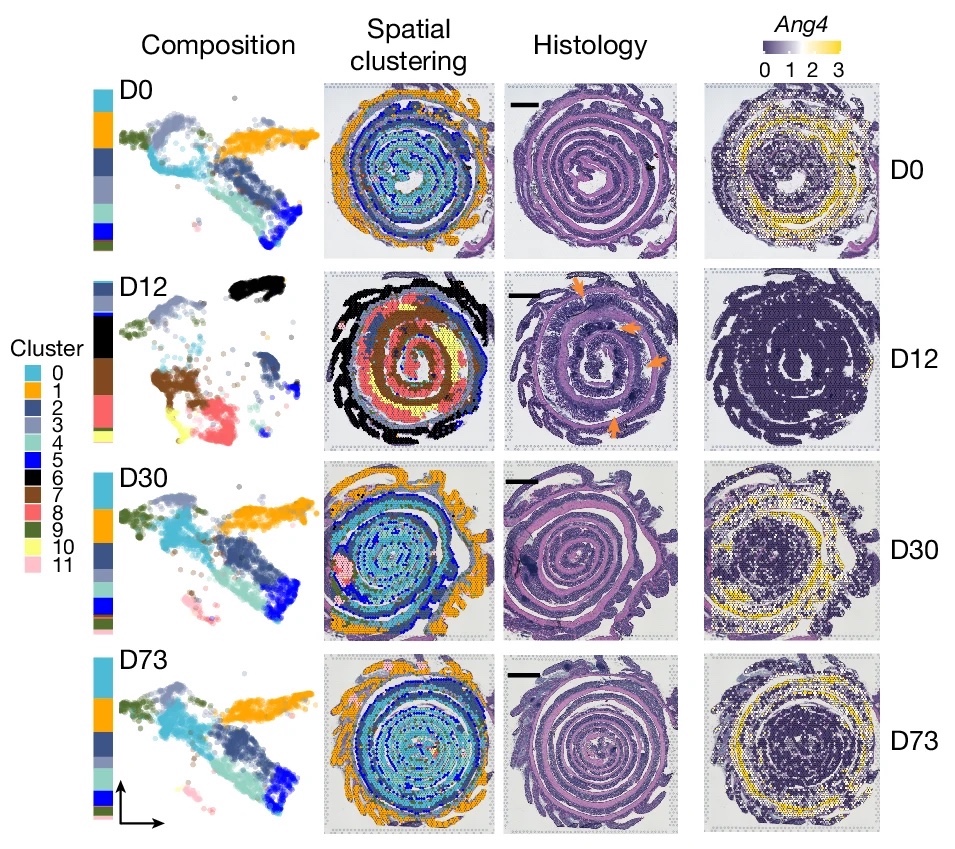
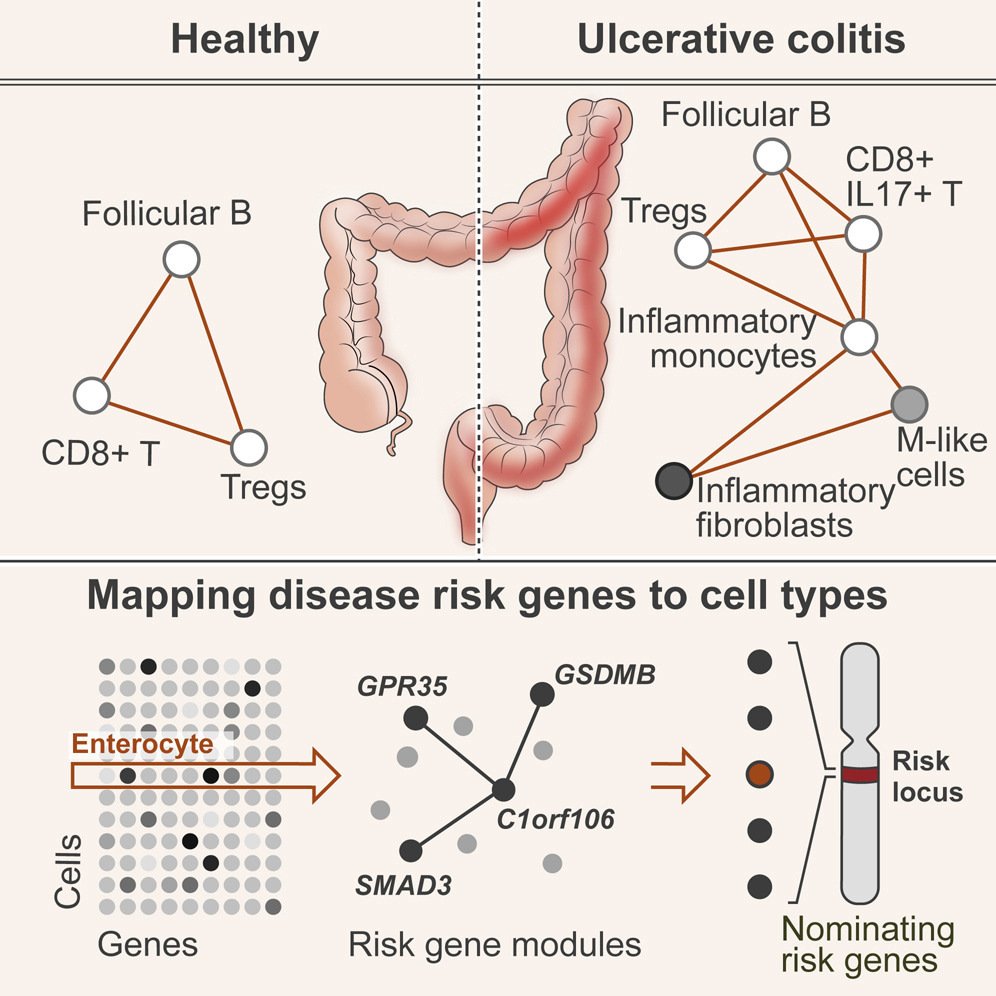
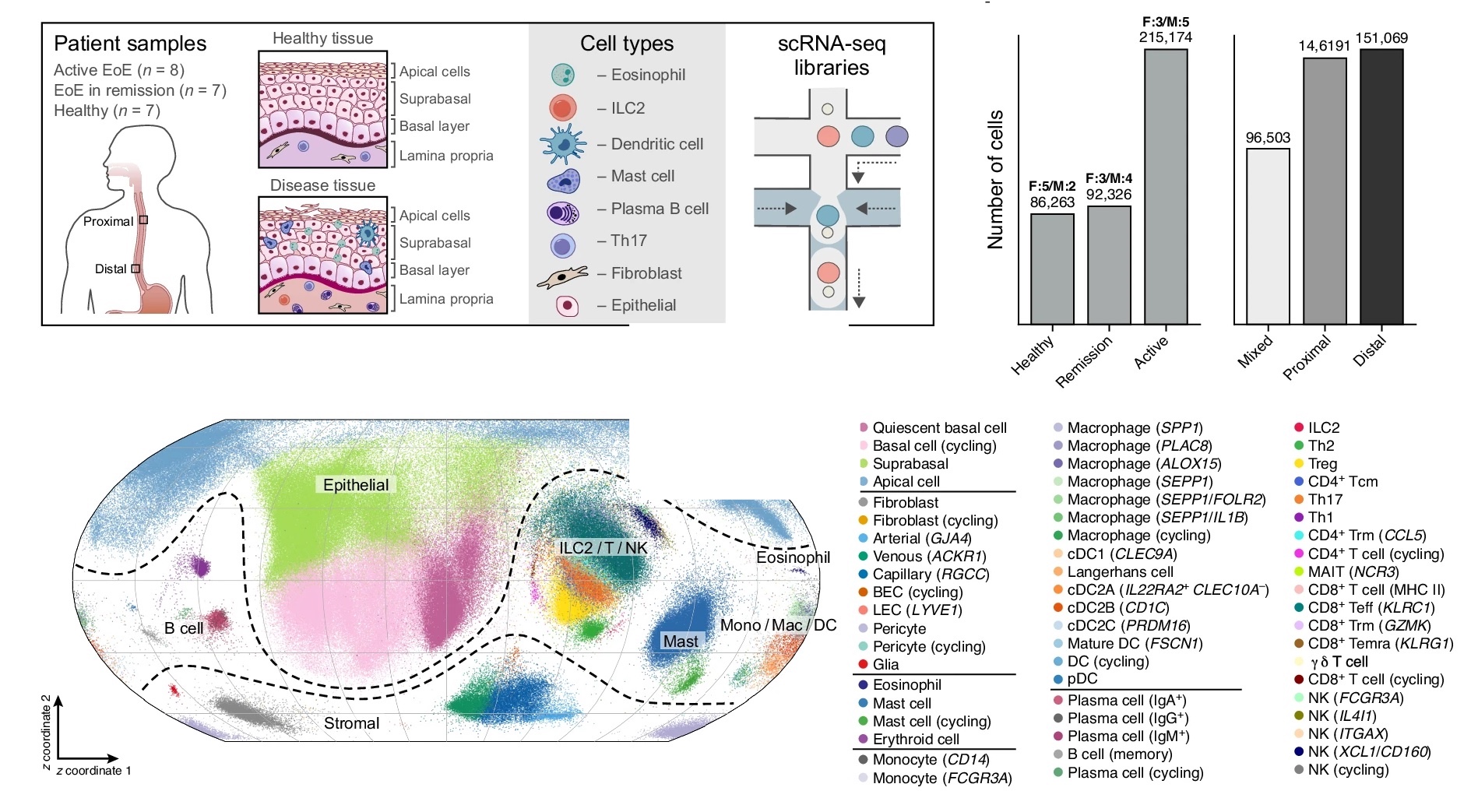
Understanding disease at the single cell level |
|---|
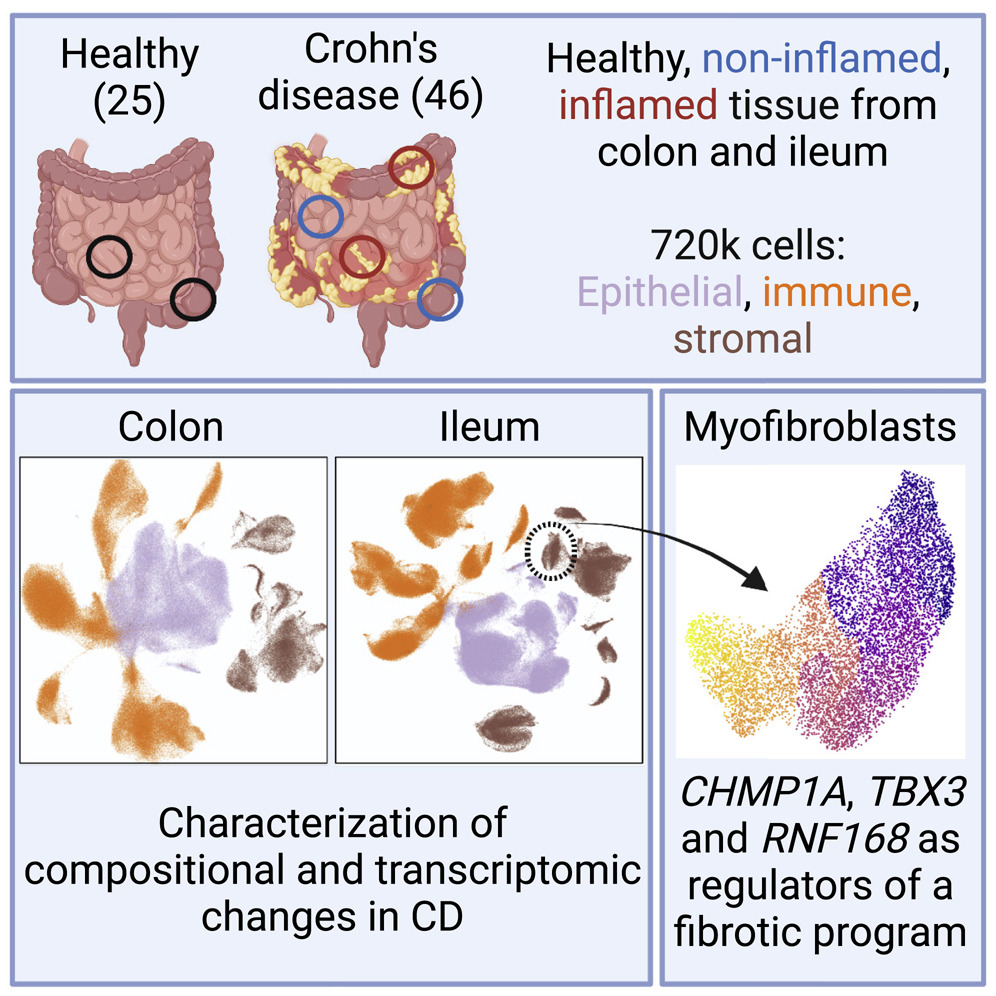
CSIBD integrative studies |
|---|