CSIBD investigators develop and share modern, sophisticated techniques to define the mechanisms contributing to IBD and digestive disease as described below.
|
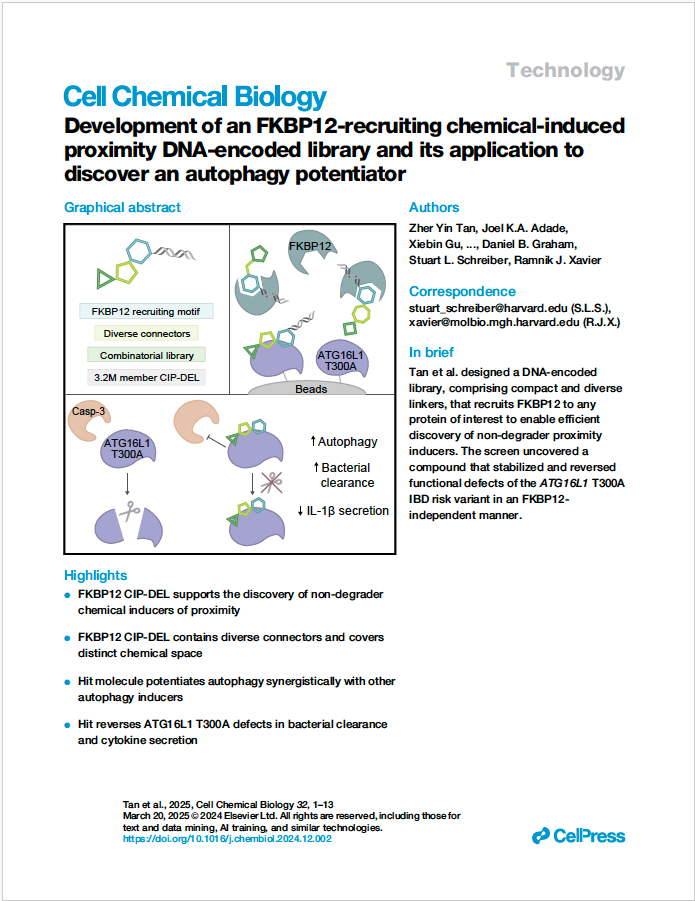
DNA-Encoded libraries (DELs) are large combinatorial libraries in which each chemical compound is encoded by a DNA tag that records its synthetic history. This DNA barcode allows compounds to be screened in a pooled format, providing an efficient way of discovering binders against various targets. A recent article from the Xavier lab and collaborators in Cell Chem Biol, describes the design and generation of a DEL that was used to identify a compound that targets a Crohn's disease-related protein and reduces its variant's detrimental effects. The sequencing data reported in this article is available on Zenodo. Compound and bioassay information is available in PubChem (1963952, 1963956, 1963957, 1963955, 1963953 and 1963954). |

|
Single cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) allows researchers to study the gene expression profile of each cell within a population, revealing cellular heterogeneity and providing a detailed look at cell-to-cell variations that wouldn't be visible with traditional bulk RNA sequencing methods. The Villani lab describes the generation of scRNAseq data from biopsy samples from single cell dissociation through sequencing and analysis in a recent publication in Nature Medicine. Their study reveals the tremendous cellular transcriptional heterogeneity underlying immune-related adverse events colitis and identify pathways for clinical diagnostics and therapeutic interventions. |

|
Spatial transcriptomics is a technique that measures gene expression levels at different locations within a tissue. It provides a map of gene expression in a tissue, which can be used to study the relationship between cells and their environment. A recent publication in Nature from the Xavier lab describes the spatial transcriptome of the gut at steady state and in response to homeostatic regulators. The authors describe their adaptation of the Swiss roll technique, a classical dimensionality reduction solution for histological study, and subsequent data generation with Visium and Xenium workflows as well as droplet-based scRNA-seq. |
